Want to know how to quickly charge a 12V deep cycle battery for your RV camping, solar energy system or boat? Whether using a 10A lithium battery charger or a standard charger, understanding charging time is crucial for efficient charging and long battery life. Below, we'll guide you through charging 12V deep-cycle batteries, such as lead-acid and lithium (LiFePO4), to provide reliable power for your adventures.

Mastering the 12V Deep Cycle Battery Charging Process
Charging a 12V deep cycle battery transfers energy from a battery charger to restore its battery capacity, measured in amp hours (Ah). Unlike starter batteries, deep cycle batteries are built for sustained backup power in solar systems, boats, or RVs.
The charging process involves three stages: bulk (constant current, 60%-80% of charging time), absorption (constant voltage), and float (trickle charger mode for maintenance).
Battery types like lead-acid batteries and lithium (LiFePO4) differ in efficiency, with lithium's Battery Management System (BMS) optimizing current for faster, safer charging.
Factors Affecting 12V Deep Cycle Battery Charging Time
Several factors influence how long it takes to charge a 12V deep cycle battery at 10 amps:
Battery Capacity: Key to Charging Time
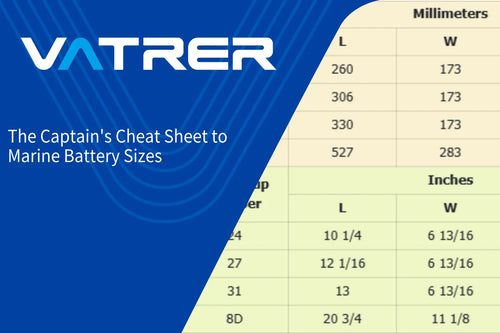
Battery capacity, measured in amp hours (Ah), determines how much energy a 12V deep cycle battery can store. A 12V 100Ah battery takes longer to charge than a 20Ah one at the same charging rate. Deep cycle batteries typically range from 50Ah to 200Ah, suiting applications like solar or RV camping. Vatrer batteries offer larger capacity models: 100Ah-560Ah, all to meet your power needs.
State of Charge: Impact on 12V Battery Charging
The initial state of charge (SOC) affects charging time. A fully discharged 12V deep cycle battery takes longer to reach full charge than a partially discharged one. For example, a 100Ah battery at 50% SOC (about 12.2V, measurable with a voltmeter) needs roughly half the time compared to a fully drained battery.
Charging Current: Speeding Up Your 12V Battery Charge
The charging rate, measured in amperes, controls how fast energy flows into the battery. A 10A lithium battery charger delivers 10 amps per hour, outpacing a 5-amp charger. Lithium batteries support higher charging rates (10A-20A or 70A) without overheating risks, unlike lead-acid batteries, but always match the rate to the battery type.
Charging Efficiency: Maximizing 12V Battery Performance
Not all energy from a battery charger is stored, some is lost as heat due to internal resistance and chemical reactions. Lead-acid batteries have 70%-85% efficiency, while lithium batteries reach 85%-95%, reducing charging time. For accurate calculations, divide theoretical time by the efficiency factor (like 0.85 for lead-acid).
Temperature: Optimizing Your 12V Battery Charging Environment
Temperature affects the charging process. Cold conditions (below 0°C) reduce efficiency by 10%-20%, while high temperatures risk overheating, shortening battery life. Lithium batteries (LiFePO4) charge efficiently from -20°C to 60°C, outperforming lead-acid batteries. Charge in a well-ventilated 15°C-27°C (60°F-80°F) environment for best results.
Calculating 12V Deep Cycle Battery Charging Time
To estimate charging time for a 12V deep cycle battery, use:
- Charging Time (hours) = Battery Capacity (Ah) ÷ Charging Current (Amps) ÷ Efficiency
- Deep cycle batteries typically range from 50Ah to 200Ah, but some solar systems using 300Ah+.
- Below are example calculations and a comparison table for lead-acid batteries and lithium (LiFePO4) batteries at 10 amps, assuming a fully discharged state. Lithium batteries charge faster due to higher efficiency (90% vs. 80% for lead-acid).
Example Calculations
- 100Ah battery at 10 amps (lead-acid, 80% efficiency): Charging Time = 100 Ah ÷ 10 Amps ÷ 0.8 = 12.5 hours
- 100Ah battery at 10 amps (lithium, 90% efficiency): Charging Time = 100 Ah ÷ 10 Amps ÷ 0.9 = 11.1 hours
- 100Ah battery at 50% SOC (lithium, 90% efficiency): Charging Time = (100 Ah × 0.5) ÷ 10 Amps ÷ 0.9 = 5.6 hours
Charging Time Comparison
The table below compares estimated charging times for 12V deep cycle batteries at 10 amps for a clearer comparison:
Lead-Acid Batteries
| Battery Capacity (Ah) | Charging Rate (Amps) | Efficiency | Estimated Charging Time (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 Ah | 10 Amps | 80% | 2.5 Hours |
| 50 Ah | 10 Amps | 80% | 6.3 Hours |
| 100 Ah | 10 Amps | 80% | 12.5 Hours |
| 200 Ah | 10 Amps | 80% | 25 Hours |
| 300 Ah | 10 Amps | 80% | 37.5 Hours |
| 400 Ah | 10 Amps | 80% | 50 Hours |
Lithium (LiFePO4) Batteries
| Battery Capacity (Ah) | Charging Rate (Amps) | Efficiency | Estimated Charging Time (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 Ah | 10 Amps | 90% | 2.2 Hours |
| 50 Ah | 10 Amps | 90% | 5.6 Hours |
| 100 Ah | 10 Amps | 90% | 11.1 Hours |
| 200 Ah | 10 Amps | 90% | 22.2 Hours |
| 300 Ah | 10 Amps | 90% | 33.3 Hours |
| 400 Ah | 10 Amps | 90% | 44.4 Hours |
Practical Tips for Efficient 12V Deep Cycle Battery Charging
- To cut charging time: Use a higher-amp charger: A 12V 10A lithium battery charger is efficient, but a 20A charger halves the time for compatible batteries (lithium). Ensure the charger matches the battery's rated current, noting higher costs.
- Charge in optimal conditions: Maintain 15°C-27°C with good ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Choosing the Right 12V Deep Cycle Battery: Lead-acid batteries (AGM, Gel) require slower charging rates to avoid damage, with AGM charging slightly faster than Gel. Lithium batteries, with built-in Battery Management Systems (BMS), support faster, safer charging. Lithium batteries (like LiFePO4) charge faster and offer 2,000-5,000 cycles vs. 200-500 for lead-acid batteries. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for your battery type.
Safety and Maintenance for 12V Deep Cycle Batteries
Avoiding Overcharging: Protecting Your 12V Battery Life
Overcharging reduces battery life and may cause capacity loss or battery swelling. Use a battery charger with automatic shut-off or a trickle charger for maintenance. Lithium batteries with BMS automatically prevent overcharging, ensuring safety.
Monitoring Your 12V Battery Charging Process
Track the charging process using a voltage meter or a 12V 10A lithium battery charger with a display. Voltages of 12.6V (lead-acid) or 13.2V (lithium) indicate near full charge, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting 12V Deep Cycle Batteries
- Lithium batteries: Avoid full discharge, check BMS status, and store at 50% SOC for longevity.
- Lead-acid batteries: Monitor electrolyte levels (if applicable) and avoid deep discharges.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for efficient charging and extended battery life.
Conclusion: Power Up Your 12V Deep Cycle Battery Efficiently
Charging a 12V deep cycle battery at 10 amps is simple with the right knowledge. Understand battery capacity, charging rates, and factors affecting charge time to optimize the charging process. Lithium batteries, with higher efficiency and BMS, outshine lead-acid batteries for faster, safer charging.
Use a 10A lithium battery charger and charge in optimal conditions for best results. Ready for reliable backup power? Check Vatrer LiFePO4 batteries and smart chargers to enhance your experience!
FAQs
Can I use a 10A lithium battery charger for both lithium and lead-acid batteries?
While a 10A lithium battery charger is optimized for lithium (LiFePO4) batteries, it may not be suitable for lead-acid batteries (AGM or Gel). Lithium chargers often lack the specific voltage profiles needed for lead-acid's absorption and float stages, which can lead to undercharging or damage.
Check the charger's specifications for compatibility with your battery type. For versatility, choose a multi-mode battery charger that supports both lithium and lead-acid, adjusting charging rates automatically. Always follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure efficient charging and avoid reducing battery life.
How do I know if my 12V deep cycle battery is fully charged without a voltmeter?
If you don’t have a voltmeter, most 12V 10A lithium battery chargers with displays show charge status (percentage or LED indicators). For lead-acid batteries, a green light or “float mode” on a trickle charger often signals full charge.
Invest in a smart charger or lithium battery with a built-in display for real-time status. Alternatively, observe the charger’s behavior—lithium chargers typically stop or reduce current significantly when the battery reaches 13.2V, while lead-acid chargers enter maintenance mode at 12.6V-12.8V. This ensures safe and efficient charging.
What should I do if my 12V deep cycle battery takes longer than expected to charge?
If your charging time exceeds calculations (such as over 12.5 hours for a 100Ah lead-acid battery at 10 amps), factors like low state of charge (SOC), cold temperatures, or a faulty charger may be at play.
First, verify the charging rate with a multimeter to ensure the 10A lithium battery charger delivers 10 amps. Charge in a 15°C-27°C environment to avoid efficiency losses. If the battery is old, test its battery capacity with a professional tester, as degradation can extend charging time. Replace the battery if capacity is below 80% of its rated amp hours (Ah).
Is it safe to leave my 12V deep cycle battery charging overnight with a 10A lithium battery charger?
Leaving a 12V deep cycle battery charging overnight is generally safe with a 10A lithium battery charger equipped with automatic shut-off or a trickle charger mode, especially for lithium batteries with a Battery Management System (BMS). However, lead-acid batteries are more prone to overcharging risks if the charger lacks smart features. Use a smart charger with overcharge protection for both battery types. For lead-acid batteries, monitor periodically to prevent capacity loss or swelling. Ensure good ventilation to avoid heat buildup, preserving battery life.
How can I extend the battery life of my 12V deep cycle battery beyond charging practices?
Beyond efficient charging, battery life depends on usage and storage habits. Frequent deep discharges or improper storage can degrade both lithium and lead-acid batteries.
For lithium batteries, maintain 20%-80% SOC during use and store at 50% SOC in a cool, dry place. For lead-acid batteries, avoid discharges below 50% and check electrolyte levels monthly (if applicable). Use a trickle charger for long-term storage to maintain full charge. Regular cycling and proper maintenance can extend battery life to 2000-5000 cycles for lithium or 200-500 for lead-acid.
Can I charge a 12V deep cycle battery faster than 10 amps, and what are the risks?
Yes, lithium 12V deep cycle batteries can often handle higher charging rates (like 20A-50A), but lead-acid batteries typically require slower rates to avoid damage. Exceeding recommended charging rates can overheat lead-acid batteries, reducing battery life.
For lithium, use a 12V 10A lithium battery charger or higher (like 20A or 70A) if the battery's specs allow, ensuring the BMS manages safety. For lead-acid, stick to 10%-20% of the battery capacity (like 10A-20A for a 100Ah battery). Always consult manufacturer guidelines to balance speed and safety.
How does a trickle charger differ from a 10A lithium battery charger for maintaining my battery?
A trickle charger delivers a low current (1A-2A) to maintain a full charge without overcharging, ideal for long-term storage of 12V deep cycle batteries. A 10A lithium battery charger is designed for faster charging but may not sustain low-current maintenance.
Use a trickle charger for lead-acid batteries during storage to prevent sulfation. For lithium batteries, a smart 10A lithium battery charger with a maintenance mode is sufficient, as the BMS prevents overcharging. Choose based on your battery type and storage needs.