What Size Battery Do I Need For My Boat? How to Choose
Reading time 9 minutes
When it comes to boating, having the right battery size is more than a convenience, it's essential for safety, performance, and efficiency. Whether you're powering a fishing boat, pontoon, or sailboat, the correct battery determines how long your devices run, how reliably your motor starts, and how smooth your trips are. This guide explains how to determine the ideal battery size, what voltage your system needs, and why many boat owners are switching to lithium options like LiFePO4 batteries for long-term savings and reliability.
Key Takeaways
- The right battery size depends on your boat's electrical load, motor voltage, and trip duration.
- Deep-cycle marine batteries are ideal for powering lights, electronics, and accessories over time.
- A typical small fishing boat uses 12V 80-120Ah batteries, while larger boats may require 24V or 48V systems.
- Lithium batteries last up to 10 years and weigh 50-70% less than lead-acid models.
- Use a simple energy calculation (Watts × Hours ÷ Voltage = Ah) to size your battery correctly.
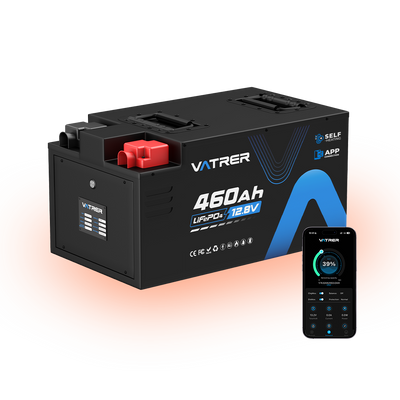
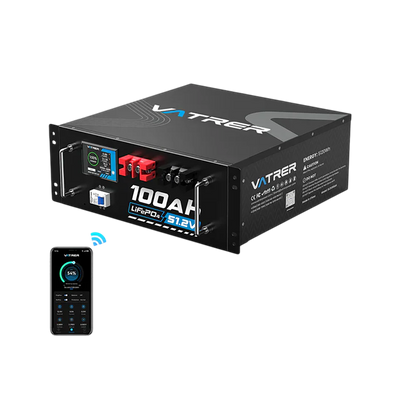
- Upgrading to a Vatrer marine lithium battery offers better efficiency, faster charging, and reduced maintenance.


Understanding Common Types of Marine Batteries
Boat batteries are not one-size-fits-all. Before deciding on what size or type you need, it's crucial to understand the different kinds available and what role each plays in your electrical system. Choosing the wrong type can shorten battery life or leave you stranded, while the right one can provide years of reliable power and peace of mind.
- Starting Batteries: Starting batteries deliver short bursts of high current to crank the engine. They recharge quickly from the alternator but aren't built for long, steady discharge. If you only need to start your motor and rely on shore power for everything else, this type might be sufficient.
- Deep Cycle Marine Batteries: These are designed to discharge power slowly and consistently, making them perfect for running accessories like fish finders, lighting, and refrigerators. They have thicker plates and can handle repeated discharge cycles, ideal for trolling motors or boats with multiple electrical systems.
- Dual-Purpose Batteries: These batteries combine engine-starting capabilities with moderate deep-cycle performance. They work best for smaller boats with limited space or moderate electrical needs.
There are three main chemical types of Marine Battery
- Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA): Affordable but heavy and requires periodic maintenance, such as water refilling.
- AGM/Gel: Sealed, spill-proof, and maintenance-free, with better vibration resistance.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): Lightweight, long-lasting, and maintenance-free, quickly becoming the preferred option for modern marine setups.
Tip: If you frequently use electronics or trolling motors, consider upgrading to a deep-cycle lithium boat battery for maximum runtime and minimal upkeep.
How to Determine What Size Battery You Need
Choosing the correct battery size starts with understanding how much energy your boat consumes in a typical outing. In boating terms, “size” refers not to physical dimensions, but to amp-hour capacity (Ah) and system voltage (V), the two key factors that dictate how long your battery can power your systems.
Step 1: List All Electrical Devices
Please make a list of all devices and their power ratings (in watts), including lights, fish finders, GPS, refrigerators, pumps, and trolling motors.
Step 2: Estimate Daily Usage
Multiply each device's wattage by the number of hours you use it per day. Add all the values to find the total energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh).
Step 3: Convert Watt-Hours to Amp-Hours
Use this simple formula:
Battery Capacity (Ah) = Total Watt-Hours ÷ System Voltage
For example, if your total load is 880Wh and your system runs on 12V:
880 ÷ 12 = ~73Ah.
Adding a 25% safety margin means you should choose at least a 100Ah deep-cycle marine battery.
Sample Boat Battery Size Chart
| Boat Type | Voltage System | Recommended Capacity (Ah) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kayak w/ trolling motor | 12V | 30–60Ah | Short trips, light load |
| Small fishing boat | 12V | 80–120Ah | Moderate load, fish finder & lights |
| Pontoon / Cabin boat | 24V | 100–200Ah | Multiple devices & longer outings |
| Sailboat / Yacht | 24V–48V | 200–400Ah+ | Heavy loads & long voyages |
Purpose of the chart: This reference helps boat owners compare typical battery sizes by vessel type and usage level, making it easier to estimate the ideal configuration before purchasing.
What Battery Voltage System Does Your Boat Need?
Your boat's voltage system determines how efficiently power is delivered and how many batteries you'll need. Choosing between a 12V, 24V, or 48V system depends on the type of boat, size of the motor, and total energy demand.
- A 12V system is the most common in small boats and trolling setups, offering simplicity and ease of use for shorter trips.
- A 24V system doubles the voltage while reducing the current draw, which improves efficiency and extends runtime for medium-sized boats.
- A 48V system is used in large or electric-powered vessels that require heavy power for long durations, minimizing cable heat and energy loss.
Higher-voltage systems are more efficient but may need compatible controllers and chargers. Always consult your motor's specifications before switching from 12V to 24V or 48V, as mismatched systems can lead to performance issues.
Lithium vs Lead-Acid: Which Is Better for Marine Use?
Choosing between lithium and lead-acid batteries is one of the most important decisions for boat owners. Each technology has its strengths and limitations, but understanding how they differ can help you make a smarter, longer-term investment.
Performance and Efficiency
Lead-acid batteries have been the standard for decades, but their usable capacity is limited, typically around 50% of total capacity. This means a 100Ah lead-acid battery effectively delivers only 50Ah before needing a recharge. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, can safely discharge up to 90-100% of their rated capacity without damage. This makes lithium significantly more efficient, offering longer runtime per charge.
Weight and Space
Lead-acid batteries are heavy and bulky due to their dense lead plates and liquid electrolyte. Lithium batteries are up to 70% lighter for the same capacity, allowing for better weight distribution and freeing up valuable onboard space. This makes a major difference for small boats where every pound counts.
Maintenance and Longevity
Lead-acid models require regular maintenance, such as water refilling and corrosion checks. They also degrade faster with deep discharges, typically lasting 300-500 cycles. Lithium batteries, especially LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate), are maintenance-free and can exceed 3,000-5,000 cycles, equivalent to over 10 years of use. They also maintain a stable voltage throughout discharge, ensuring consistent performance for electronics and motors.
Safety and Charging
Lithium marine batteries come with built-in Battery Management Systems (BMS) that protect against overcharging, short-circuiting, and extreme temperatures. They also charge faster, typically in 3-5 hours compared to 8-12 hours for lead-acid. In contrast, flooded lead-acid batteries can leak acid or emit gases, requiring careful ventilation and handling.
Lead-Acid vs. Lithium (LiFePO4) Comparison Table
| Feature | Lead-Acid Battery | Lithium (LiFePO4) Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavy | 50–70% lighter |
| Cycle Life | 300–500 cycles | 3,000–5,000+ cycles |
| Maintenance | Requires refilling | Maintenance-free |
| Charging Time | 8–12 hours | 3–5 hours |
| Depth of Discharge | 50% usable | 90–100% usable |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Lower lifetime cost |
Therefore, for boat owners who prioritize reliability, longevity, and ease of use, a Vatrer marine lithium battery is the superior choice. It delivers higher energy density, faster charging, and a much longer lifespan, ideal for trolling motor systems or long-distance cruising.
Common Battery Sizes Used in Different Boats
Different boats have unique power requirements, and understanding real-world configurations can help you make a practical decision. Battery size depends on your boat type, the equipment you power, and how long you stay on the water.
- Fishing Boat(55 lb thrust motor): 12V 100Ah lithium battery provides about 4-6 hours of trolling operation.
- Pontoon Boat(fridge, stereo, lighting): 24V 200Ah system offers balanced power and runtime for leisure activities.
- Sailboat(navigation, lighting, refrigeration): 48V 300Ah setup supports long voyages with multiple onboard systems.
Tip: Use a boat battery capacity calculator to fine-tune your selection based on equipment wattage and expected runtime before purchasing.
How to Choose the Right Boat Battery Size
Selecting the best battery for your boat involves more than just capacity, it's about compatibility, safety, and performance. A proper choice ensures your devices run smoothly without overloading your system.
Key Factors to Consider
- Capacity (Ah): Determines how long your equipment can run before recharge.
- Voltage: Must match your motor and onboard electronics.
- Weight & Dimensions: Ensure the battery fits properly without upsetting boat balance.
- Durability & Safety: Look for IP67 or higher waterproof ratings and vibration resistance.
- Charging Options: Confirm compatibility with your onboard or solar chargers.
- Maintenance: Lithium models eliminate water checks and corrosion cleaning.
If your setup involves multiple accessories or longer trips, a deep-cycle marine battery, preferably lithium, is a reliable long-term investment.
How to Upgrade or Install the Right Battery
Upgrading or replacing your marine battery is straightforward if done correctly. The key is preparation, safety, and ensuring your system remains compatible.
- Disconnect Power: Always turn off all devices and isolate the old battery.
- Check Polarity: Match positive and negative terminals before reconnecting.
- Use a Compatible Charger: LiFePO4 batteries require specific chargers for optimal performance.
- Secure the Battery: Fasten it firmly to minimize vibration and moisture exposure.
- Ventilation: Even sealed batteries benefit from airflow to maintain an ideal temperature.
If converting from lead-acid to lithium, verify your motor and accessories support the new voltage and charge profiles. Consult the lithium battery manufacturer installation guide for best results.
Do Boat Motors Have Specific Battery Requirements?
Yes. Different motor thrust levels require specific voltages and capacities to perform optimally. Choosing the wrong combination can limit performance or even damage components.
| Motor Thrust | Recommended Voltage | Minimum Capacity (Ah) | Example Setup |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30–40 lb | 12V | 60–100Ah | Small kayak or Jon boat |
| 50–60 lb | 24V | 100–150Ah | Medium trolling motor |
| 80+ lb | 48V | 200Ah+ | Large pontoon or offshore vessel |
Always check your motor manufacturer's manual for battery specifications. Correct matching ensures maximum thrust and longer operational life for both motor and battery.
Why You Should Consider Upgrading to Lithium
Modern boaters are increasingly adopting lithium marine batteries due to their numerous advantages over traditional systems. They are lighter, safer, and offer long-term value that easily justifies the upfront investment.
- Lightweight Design: Reduces overall boat weight, improving speed and efficiency.
- Longer Lifespan: Over 10 years of dependable use with 3,000-5,000 charge cycles.
- Fast Charging: Fully recharges in half the time compared to lead-acid.
- High Energy Density: More power from a smaller, compact battery pack.
- Eco-Friendly: No acid, fumes, or lead, and completely recyclable materials.
A Vatrer marine lithium battery features advanced BMS protection, ensuring stable operation in harsh marine environments. It's ideal for those upgrading or replacing a lithium battery for trolling motor systems or for boats needing a long, uninterrupted power supply.
Conclusion
Choosing the right battery size for your boat ensures consistent power, longer runtime, and peace of mind on the water. Start by calculating your energy needs, matching the correct voltage system, and considering a LiFePO4 lithium battery for its long-term advantages.
For boaters who value reliability and performance, Vatrer marine lithium batteries deliver durable, efficient, and maintenance-free energy. Whether you're fishing, cruising, or exploring offshore, Vatrer helps you power your next journey with confidence, lightweight, long-lasting, and built for the sea.
Share